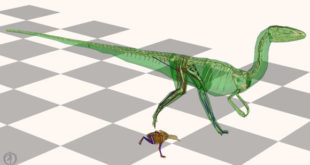
The tail of bipedal non-avian dinosaurs played a role analogous to the swinging arms of humans during walking and running, according to new research led by Harvard University’s Dr. Peter Bishop. Computer simulations of running locomotion in a modern tinamou bird (brown) and the extinct theropod dinosaur Coelophysis (green). Gray …
Read More »Tardigrades Walking
Tardigrades utilize a tetrapod-like stepping pattern remarkably similar to that observed in insects, despite significant disparities in size and skeletal structure between the two groups, according to new research led by scientists from Rockefeller and Princeton Universities. Hypsibius exemplaris. Image credit: Tarushika Vasanthan & Jonathon Stone, doi: 10.22120/jwb.2020.96855.1037. The vast …
Read More »Vocal Learning Avians
An international team of scientists led by Flinders University has found evidence of prenatal auditory learning in embryos of three vocal learning species (superb fairy-wren, red-winged fairy-wren and Darwin’s small ground finch) and two vocal non-learning species (little penguin and Japanese quail). Colombelli-Négrel et al. demonstrate a capacity to perceive …
Read More »Fish Neck-Like Motion
Trout and frogfish can bend their spines and heads upwards, despite having different anatomy from humans and other land-dwelling vertebrates, according to a study by University of Liverpool’s Dr. Ariel Camp. Craniovertebral skeleton of the Commerson’s frogfish (Antennarius commerson). Image credit: Ariel L. Camp, doi: 10.1098/rspb.2021.1091. Dr. Camp used X-ray …
Read More »Tardigrades Resembling Insects
Tardigrades utilize a tetrapod-like stepping pattern remarkably similar to that observed in insects, despite significant disparities in size and skeletal structure between the two groups, according to new research led by scientists from Rockefeller and Princeton Universities. Hypsibius exemplaris. Image credit: Tarushika Vasanthan & Jonathon Stone, doi: 10.22120/jwb.2020.96855.1037. The vast …
Read More »Great Apes Use Signals
In a paper published this week in the journal iScience, an international team of researchers documented chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and bonobos (Pan paniscus) purposefully using signals to start and then end social activities, a behavior not seen outside of the human species until now. Joint action structure of chimpanzees and bonobos …
Read More »Fasting Can Protect From Infections
Fasting before and during exposure to invasive food-borne bacteria protects mice from developing a full-blown gastrointestinal infection, in part through the actions of the gut microbiome, according to new research led by University of British Columbia scientists. Graef et al. highlight how food intake controls the complex relationship between host, …
Read More »Coronavirus Epidemic
The genomes of multiple East Asian populations bear the signature of a viral epidemic that occurred approximately 900 generations, or 25,000 years (28 years per generation) ago, according to a new study published in the journal Current Biology. Souilmi et al. apply evolutionary analyses to human genomic datasets to recover …
Read More »High Milk Intake
In a new meta-analysis of previous studies, a team of researchers from the United Kingdom, Australia and New Zealand found that people who regularly drank high amounts of milk had lower levels of both good and bad cholesterol, although their body mass index (BMI) levels were higher than non-milk drinkers; …
Read More »Tiny Mountains on Neutron Stars
Physicists are still arguing over whether black holes have “hair,” but we’re pretty sure neutron stars have mountains. These dead stars are extreme in every respect, from their magnetic field to gravitational influence, but the only thing extreme about the mountains is how small they are. A new analysis of …
Read More » #Bizwhiznetwork.com Innovation ΛI |Technology News
#Bizwhiznetwork.com Innovation ΛI |Technology News